Program design and implementation
At SCIDaR, we are committed to designing and implementing programs to create long-lasting, meaningful change. Per our culture of excellence, we also value measuring and learning from our programming’s results and effectiveness to apply insights drawn from one project to another to influence our staff, program participants, local stakeholders, and the broader development community and policymakers through our thought leadership.
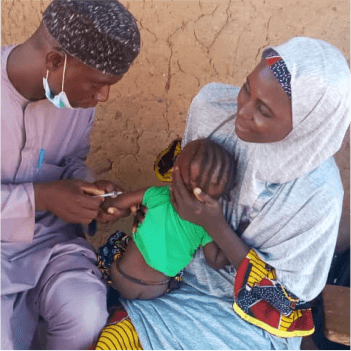
Northern Nigeria Routine Immunization and PHC Strengthening Program (NNRISP)
Since 2014, SCIDaR with support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation has been providing analytical, programmatic, and thought leadership support to the Primary Health Care Development Agencies (NPHCDA) of six Northern Nigeria states, including Kano state on Routine Immunization systems strengthening. The rollout of interventions across these states commenced with a rigorous diagnostic assessment of the states’ routine immunization system to identify existing gaps that informed the RI strengthening strategies.
Smiles For Mothers
Nigeria has the highest burden of maternal deaths worldwide and more than one in five maternal deaths in Nigeria (22%) is attributable to postpartum haemorrhage (PPH).
Despite the country’s roadmap for accelerated reduction of maternal and neonatal mortality, launched by the Federal Ministry of Health in 2019 which seeks to tackle PPH-related deaths, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic risks exacerbate the number of maternal deaths and further derails Nigeria’s efforts towards contributing to SDG 3.1


Action To Control HIV Epidemic Via Evidence (ACHIEVE)
The ACHIEVE project commenced on 1st Oct 2017 with 2 states (FCT, Nasarawa) and has expanded to include Rivers states with the Scope of Work to identification and enrol into ARV care, people living with HIV using a unique private health sector approach, provide the Prevention of Mother To Child Transmission of HIV infections, ensure patient retention and quality care, support to PLHIVs who access care via private health facilities, support PHFs to ensure drug adherence and viral suppression of PLHIVs retained in care, and strengthen the health system of private health sector via continuous capacity building of the health workforce.
Gavi Guinea Bissau LMC Intervention
The Guinea Bissau MP team supported a management partner in Guinea Bissau to support its Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) team. The support centres on building the team’s leadership and management capacity through in-class sessions, one-on-one coaching sessions, and capstone projects. The project started in April 2019 and ended in July 2021.
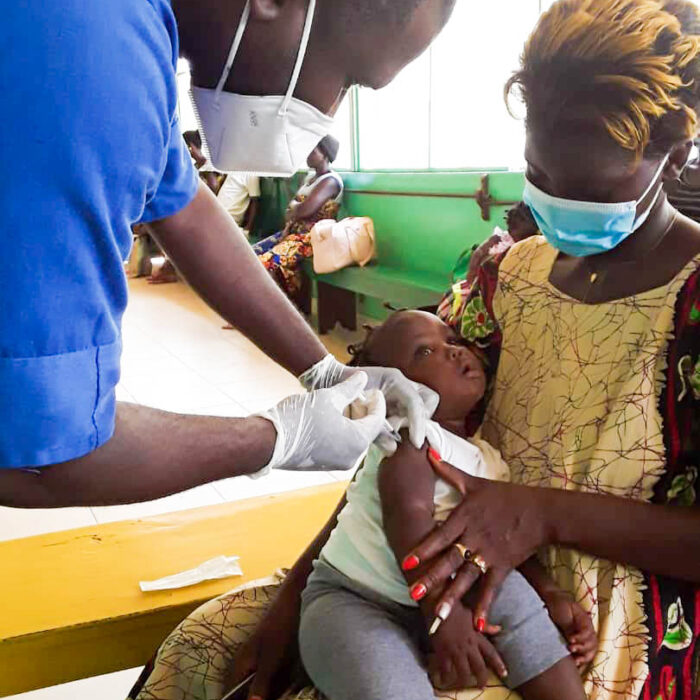

Accelerating control of the HIV Epidemic in Nigeria (ACE)
In collaboration with The Center for Clinical Care and Clinical Research (CCCRN) and Georgetown Global Health Nigeria (GGHN), SCIDaR is developing the sustainable capacity of the government to finance HIV care and treatment, as well as strengthening the capacity of Private Sector Providers (PSPs) (private clinics, laboratories, pharmacies, patent medicine vendors) and sustainable capacity of local private sector organisations including Community-based organisations (CBOs), Civil service organisations (CSOs), Faith-based organisations (FBOs)/Facilities. Within the next five (5) years, our team will provide this support for ACE-4 in Kwara and Niger States, as well as ACE-2 in Bauchi, Jigawa, and Kano States.
GAVI Health Strengthening System
Our team currently supports 6 states in Nigeria (Gombe, Jigawa, Katsina, Kebbi, Taraba and Zamfara) to develop the respective Programme Support Rationale (PSR) and situation analysis cutting across six key themes (Leadership, Management and Coordination, Service delivery, Demand Generation, Data management and disease surveillance, Human resource for health, and Vaccine supply chain and Logistics


Accelerating Nutrition Results In Nigeria (ANRiN)
Since 2017, SCIDaR has helped pregnant women access essential maternity services, promote good nutrition during pregnancy and the first two years of a child’s life by promoting breastfeeding, evidence-based complementary feeding practices, engaging parents in community conversations about health and wellness, and sensitizing men to adopt positive communication strategies and make shared household decisions about infant and child feeding with their partners.
Action to Sustain Precision and Integrated HIV Response towards Epidemic Control (ASPIRE)
Solina Centre for International Development and Research (SCIDaR) currently implements a 12-month project aimed at achieving epidemic control through providing quality HIV services to people living with HIV across FCT, Nasarawa and Rivers states. The ASPIRE project involves technical assistance and mentorship to facilities staff providing HIV testing services, antiretroviral drugs, and care and support services to people living with HIV. Being a health implementation project, SCIDaR seeks to adequately support the facilities for better patient outcomes, thereby contributing to the overall epidemic control on a larger scale, while also interacting with other stakeholders in the state with similar goals.


Nigerian Learning Collaborative (NLC) Project
The Gates Foundation and other donors have galvanised stakeholders to establish the Global Learning Collaborative to Advance Normative Change as part of efforts to improve programming and research that addresses social norms.
The Nigerian Learning Collaborative, modelled after the Global Collaborative, was established in 2020 as a country-level Community of Practice (CoP). It draws participants from government organisations, donor agencies, NGOs, and academia to strengthen networks, build sustained expertise and capacity in Nigerian organisations and institutions, and support good quality programming.
The Typhoid Vaccine Acceleration Consortium (TyVAC)
The Typhoid Vaccine Acceleration Consortium (TyVAC) has identified Nigeria as a priority country for the introduction of new typhoid conjugate vaccines (TCVs) in order to reduce the burden of typhoid. As a member of TyVAC, PATH is focused on providing new evidence related to typhoid disease burden, antimicrobial resistance, cost-effectiveness, health impact analyses, and data to support the introduction of TCV in Nigeria.
To achieve this goal, PATH has engaged the Solina Centre for International Development and Research (SCIDaR) to collate data and evidence for the advocacy and engagement of decision-makers in Nigeria.


FOR M(om) Project
The FOR M(om) initiative aims to enhance maternal healthcare and reduce maternal mortality rates in 250 public and private healthcare facilities across Delta, Lagos, and Kano states in Nigeria. The initiative is being led by MSD for Mothers, which has partnered with a consortium comprising Helium Health, SCIDaR, and AFRIDA.
The consortium will work to improve the quality of maternal care by enabling public and private healthcare facilities to access financing to enhance their maternal services. Additionally, they will implement systems-strengthening interventions that include capacity building of healthcare workers, digitisation of patient health records, and community engagement to amplify and sustain the impact of the health facility financing.
Expanded Special Project for Elimination of NTD (ESPEN)
Solina in partnership with eHealth Africa is implementing the ESPEN project created through a joint venture by BMGF and the WHO regional office for Africa (WHO AFRO) to accelerate the control and elimination of the five most prevalent NTDs and ensure the availability of quality data for neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) surveillance, management, and control. The ESPEN portal was the first of its kind to publicly share sub-national data on NTDs consistently for all 48 countries in the AFRO region and has proven resourceful in the strategic NTDs elimination efforts.


Sustaining Action for Gender Equality (SAGE)
Gender mainstreaming, driven by the Beijing Declaration, is a global strategy for promoting equality. Despite efforts, the 2022 Sustainable Development Goals report highlights insufficient progress, with women underrepresented in the global workforce and managerial positions. Nigeria’s Gender Development Index indicates persistent gender inequality, influenced by patriarchal norms.
In 2020, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation initiated the Gender Equality Division (GED), supporting organisations like SCIDaR to mainstream gender across programs. SCIDaR acknowledges the importance of diversity and aims to enhance its gender integration efforts.
Monitoring learning & evaluation for targeted Performance management of subnational tailoring (SNT) in Nigeria
Nigeria accounts for 27% of the global malaria burden and 32% of malaria deaths globally1. Despite improvements in Nigeria’s malaria performance observed from the NDHS 2021, systemic gaps in Nigeria’s malaria response hinder the attainment of national malaria elimination targets.
WHO, partners and the NMEP have developed a stratified intervention mix to guide targeted efforts toward malaria elimination. The analysis covers all states in Nigeria, down to the local government levels. However, a challenge arises because the states lack control over resources and decision-making, which hampers the effective utilization of the intervention mix to guide state-level malaria plans.

BMGF SPARK (Strengthening PHC and reaching unimmunized kids)
The SPARK project is aimed at providing differentiated system-strengthening support to the Ministries of Health in seven northern Nigeria states: Bauchi, Borno, Kaduna, Kano, Sokoto, Yobe, and Zamfara. The goal of the program is to assist the State Primary Health Care Development Agencies (SPHCDAs) in leveraging Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) funds and making significant gains in primary healthcare (PHC) and routine immunization (RI) coverage.
SPARK is focussed on strengthening planning and coordination for the PHC program to drive effective data-driven and gender-responsive resourcing, performance management, and accountability.
Social Norms and Agency Learning Collaborative (SNALC)
Nigeria accounts for 27% of the global malaria burden and 32% of malaria deaths globally1. Despite improvements in Nigeria’s malaria performance observed from the NDHS 2021, systemic gaps in Nigeria’s malaria response hinder the attainment of national malaria elimination targets.
WHO, partners and the NMEP have developed a stratified intervention mix to guide targeted efforts toward malaria elimination. The analysis covers all states in Nigeria, down to the local government levels. However, a challenge arises because the states lack control over resources and decision-making, which hampers the effective utilization of the intervention mix to guide state-level malaria plans.

Routine Immunization Strengthening Program (Chad, Africa)
In this project, Solina helps increase the access and coverage of routine immunization in the provinces of Hadjer-Lamis, Kanem and Lac in Chad. The team supports the Project Management Unit (UGP) and Directorate of Vaccination to effectively and sustainably manage the Routine Immunization (RI) program. Solina has been able to sustain and improve the timeliness of immunization funds disbursement to the three provinces, sustain the conduct of financial justification and validation of funds disbursed to the provinces, health districts and health centres, and take delivery of all MoU-funded procurements and distribute across all administrative levels.


